In a world where cars are becoming smarter and faster, 3D printing is revving up the automotive industry like never before. Imagine whipping up a custom part for your ride faster than you can say “vroom vroom.” This technology isn’t just for creating quirky trinkets; it’s revolutionizing how manufacturers design, produce, and even repair vehicles.
Gone are the days of waiting weeks for a replacement part. With 3D printing, it’s all about speed and efficiency, making the automotive process as smooth as a freshly paved road. From prototypes to production, this innovative approach is driving the future of transportation. Buckle up as we explore the thrilling intersection of 3D printing and automotive engineering, where creativity meets practicality, and the possibilities are as limitless as the open road.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of 3D Printing for Automotive
3D printing revolutionizes the automotive sector by streamlining the production process. It allows manufacturers to design and create custom parts with precision, enhancing vehicle performance. This technology facilitates rapid prototyping, enabling faster development cycles for new vehicle models.
Cost efficiency stands out as a major advantage. Traditional manufacturing often involves expensive tooling and long lead times. In contrast, 3D printing reduces material waste and allows on-demand production, significantly lowering costs.
Flexibility in design enhances innovation. Engineers can test and refine complex geometries quickly. Many automotive companies utilize this capability to explore new designs that were previously impractical or impossible.
The integration of 3D printing into supply chains improves logistics. Parts can be produced closer to assembly locations, reducing shipping times. Just-in-time production minimizes inventory costs, aligning with modern lean manufacturing practices.
Customization opportunities expand with 3D printing. Customers increasingly demand personalized features in their vehicles. This technology meets those needs without the significant costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
Sustainability also benefits from 3D printing advancements. Manufacturers adopt eco-friendly materials, contributing to reduced environmental impact. Many companies leverage this method to create lighter parts, improving fuel efficiency and lowering emissions.
Overall, 3D printing not only streamlines manufacturing but also fosters innovation and sustainability in the automotive industry. It brings together creative design and practical application, shaping the future of vehicle production and repair.
Advantages of 3D Printing in the Automotive Industry
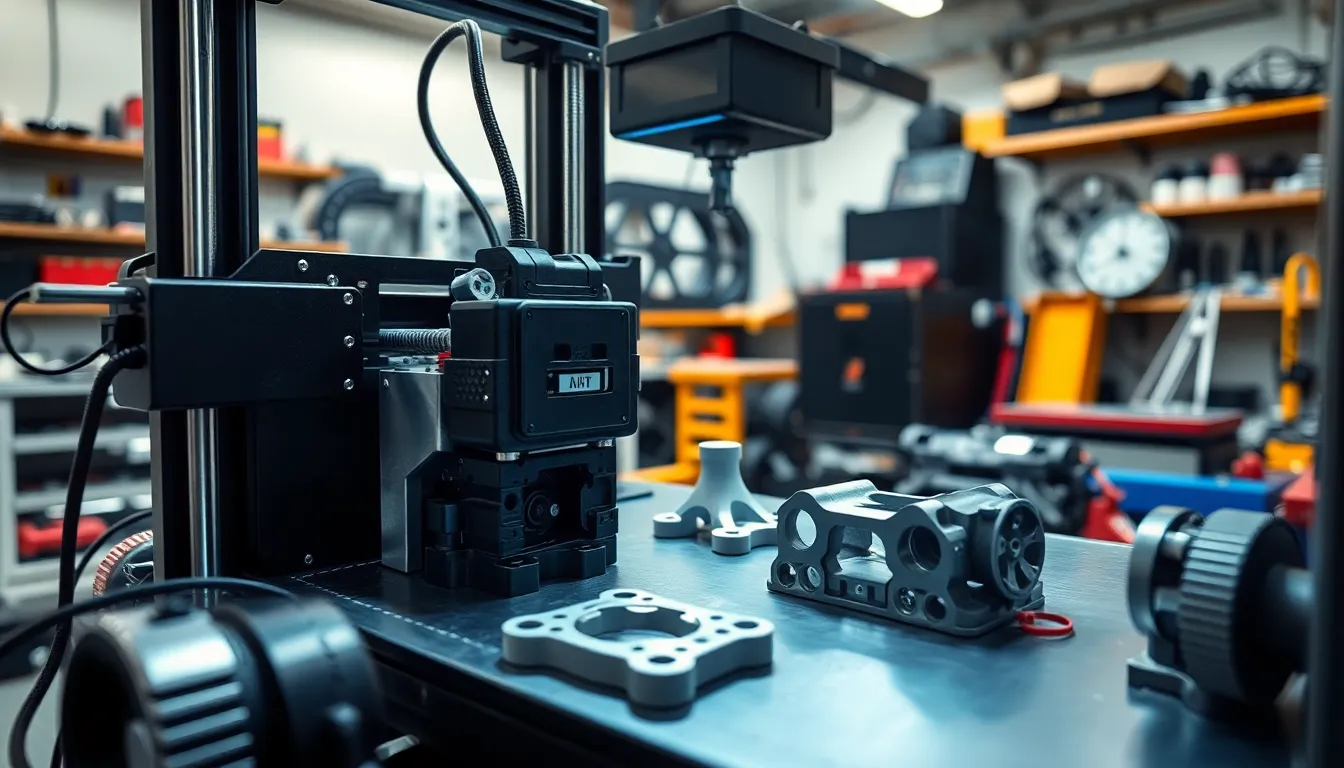

3D printing significantly enhances the automotive industry’s efficiency and innovation. Its ability to produce intricate and unique parts aligns perfectly with today’s fast-paced market.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Customization remains a key benefit of 3D printing in automotive applications. Designers can create tailored components that suit specific vehicle models. Complex shapes that were previously difficult or costly become achievable, promoting creativity in design. Rapid prototyping enables engineers to test designs promptly, refining them based on real-time feedback. Such flexibility allows brands to meet consumer demands for personalized vehicles without extensive delays.
Cost Efficiency and Material Waste Reduction
Cost efficiency stands out as another vital advantage of 3D printing. Traditional manufacturing processes often lead to significant material waste, while 3D printing optimizes material usage. By producing parts on demand, manufacturers minimize excess inventory, reducing costs associated with storage and overproduction. Overall, this technology leads to lower production costs while maintaining high-quality standards, making it an attractive option for automotive companies aiming to stay competitive.
Applications of 3D Printing for Automotive
3D printing significantly impacts the automotive sector by streamlining processes across various applications.
Prototyping and Product Development
Designers use 3D printing for rapid prototyping, which accelerates the development cycle. Engineers can quickly transform digital models into physical components, allowing for immediate testing and validation. Iterative design becomes more efficient since feedback can lead to swift modifications. Various materials, such as plastics and metals, cater to different design requirements, enhancing versatility. Custom parts often emerge from this process, promoting creativity while minimizing costs. Manufacturers reduce time to market, gaining a competitive edge in the automotive space. Rapid prototyping ensures that vehicles meet consumer expectations, fulfilling both functionality and aesthetic needs.
Production Parts and Tooling
Production parts benefit from 3D printing due to its ability to create complex geometries that traditional methods struggle with. Tooling, such as jigs and fixtures, can be produced on-demand, lowering lead times and costs. Manufacturers reduce material waste by utilizing additive manufacturing processes for efficient part creation. Parts produced through 3D printing often weigh less, contributing to improved fuel efficiency in vehicles. Customization occurs easily, ensuring that components fit specific vehicle models perfectly. This technology supports just-in-time manufacturing, optimizing inventory management. Automated processes lead to consistent quality, enhancing overall performance in automobile production.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing for Automotive
Despite its advantages, 3D printing for automotive presents several challenges and limitations. Addressing these obstacles is crucial for maximizing the potential of this technology.
Material Limitations
Materials used in 3D printing often fall short in meeting the mechanical and thermal properties required for automotive applications. Common plastics provide flexibility but lack the strength needed for structural components. Metals suitable for printing offer better durability, yet they may present difficulties in processing and cost. Engineers frequently seek advanced materials that can withstand harsh environments, ensuring both reliability and performance. The search for composite materials continues as they may improve the range of applications. For many automotive manufacturers, the limitations of available materials slow down the adoption of 3D printing technology.
Regulatory and Standards Compliance
Adhering to regulatory standards poses a significant challenge for 3D printing in the automotive sector. Various regulations govern safety, emissions, and quality control. Manufacturers often face hurdles related to proving that 3D printed parts meet these stringent requirements. Each market may impose different standards, complicating the compliance process further. Achieving certification for components created through additive manufacturing can prolong development timelines, impacting production schedules. Manufacturers must invest considerable effort in research and documentation to navigate these complexities effectively.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Automotive
3D printing holds potential to reshape the automotive landscape. Next-generation advancements focus on material innovations and technological integrations.
Innovations in Materials and Techniques
New materials enhance performance and durability in automotive applications. Researchers explore advanced composites that offer lightweight properties while maintaining strength. Innovative techniques like multi-material printing create complex component designs not feasible with traditional methods. Adoption of bio-based plastics promotes sustainability and reduces environmental impact. These advancements enable manufacturers to produce high-quality custom parts efficiently.
Integration with Other Technologies
Collaboration with AI and machine learning improves design processes and production efficiency. Smart manufacturing systems leverage data analytics to optimize 3D printing workflows. Integrating IoT technologies streamlines communication across supply chains, enhancing inventory management. Additionally, using augmented reality in design reviews accelerates validation and testing phases. This tech convergence fosters a cohesive approach to vehicle development, improving overall performance and reducing time to market.
3D printing is undeniably reshaping the automotive landscape. Its ability to produce custom parts rapidly and efficiently not only enhances creativity but also aligns with the industry’s push for sustainability. As manufacturers embrace this technology, they’re discovering new ways to improve vehicle performance while reducing costs and waste.
The integration of advanced materials and innovative techniques will likely open even more doors for customization and efficiency. As challenges like material limitations and regulatory compliance are addressed, the future of automotive 3D printing looks promising. This technology is set to revolutionize how vehicles are designed and manufactured, paving the way for a more innovative and sustainable automotive industry.