In a world where cars are no longer just metal boxes on wheels, 3D printing is revving up the automotive industry like never before. Imagine a factory where parts are printed faster than you can say “assembly line.” From prototypes to custom components, this technology is shifting gears and leaving traditional manufacturing in the dust.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of 3D Printing for Automotive Industry
3D printing significantly impacts the automotive industry by enhancing production capabilities. This technology enables the creation of complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve. Manufacturers streamline operations by using 3D printing for rapid prototyping, allowing quicker design iterations.
Cost efficiency plays a critical role in the adoption of 3D printing. Tooling expenses decrease when producing low-volume parts, making customized components more accessible. Various materials such as polymers, metals, and composites adapt well to 3D printing processes, offering flexibility in design and functionality.
Additionally, 3D printing fosters innovation within automotive design. Designers experiment with lightweight structures, improving fuel efficiency and performance. It encourages collaboration between engineers and designers, leading to more creative solutions tailored to specific vehicle models.
Significantly, automotive companies report reduced lead times. Parts that once took weeks to manufacture can often be produced in a matter of hours. This rapid turnaround supports just-in-time manufacturing models, minimizing inventory costs and waste.
Furthermore, some manufacturers capitalize on 3D printing for end-of-life vehicle solutions. Reusing materials extracted from vehicles enhances sustainability efforts. It creates a circular economy within the industry, advancing eco-friendly practices.
Advancements in 3D printing technology position it at the forefront of automotive production. Innovative applications and ongoing research drive continued growth in this area, paving the way for future developments that redefine automotive manufacturing.
Applications in Automotive Manufacturing
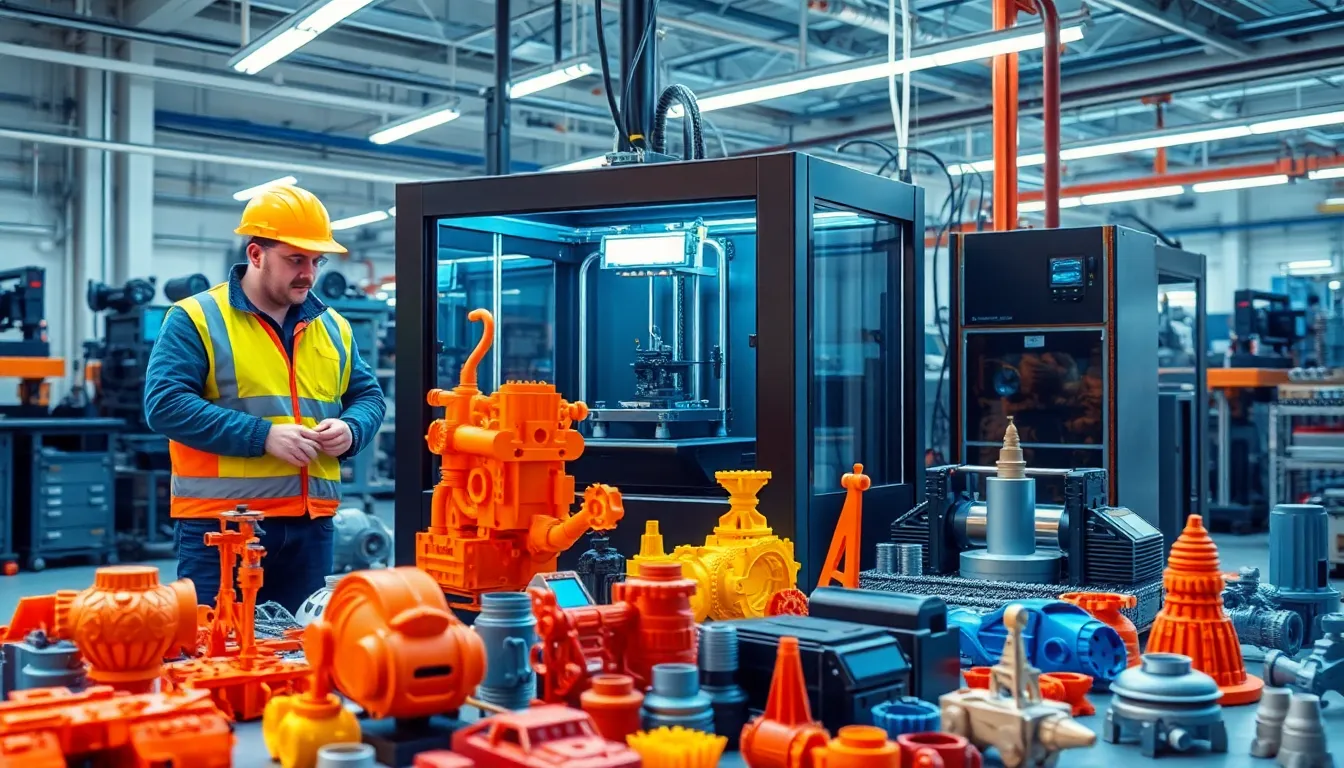

3D printing finds extensive application in automotive manufacturing, disrupting traditional production methodologies with its speed, cost-efficiency, and innovative potential.
Prototyping and Design
Prototyping benefits immensely from 3D printing technology. Designers rapidly create prototypes, reducing development time from months to weeks. Multiple iterations can occur simultaneously, accommodating real-time feedback from engineers. This agile process fosters collaboration between design and engineering teams. Select materials offer realistic evaluations of product functionality, enabling accurate assessments before full-scale production. Consequently, 3D printing significantly expedites product development cycles, allowing for faster market entry. Additionally, it’s possible to achieve complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to replicate, enhancing design possibilities.
Production Parts and Components
Production parts also significantly leverage 3D printing advancements. Manufacturers produce low-volume, custom components without large initial investments in tooling. The ability to print on demand reduces inventory costs and waste, supporting just-in-time manufacturing practices. Various materials, including metals and composites, provide manufacturers with flexibility in part specifications. Moreover, specific automotive parts, such as brackets and fixtures, benefit from weight reductions, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency. Short lead times enable automotive companies to respond swiftly to market changes and customer demands, promoting adaptability. 3D printing’s role in producing end-use components emphasizes its importance in the automotive sector.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Automotive
3D printing offers significant advantages in the automotive industry. Key benefits include cost reduction and increased design flexibility.
Cost Reduction
Cost efficiency marks a major benefit of 3D printing. Traditional manufacturing often requires expensive tooling and large production runs. In contrast, 3D printing eliminates these costs, making it economical for low-volume parts. Automotive manufacturers can create prototypes and custom components at a fraction of the price. The technology produces items on demand, reducing inventory and associated costs. By minimizing waste, companies further enhance their cost-saving efforts. With the ability to adapt production to specific needs, overall financial burdens decrease, allowing for reallocation of resources towards innovation.
Increased Design Flexibility
Design flexibility transforms automotive engineering processes. With 3D printing, complex geometries become easily achievable, which traditional methods struggle to accommodate. Designers can explore creative solutions without the constraints of conventional manufacturing processes. This technology allows for rapid iterations, enabling quick adjustments to designs. As a result, engineers and designers collaborate effectively, iterating concepts in real-time. Customization flourishes, meeting unique customer demands and preferences. Enhanced design capabilities ultimately influence vehicle performance, improving efficiency and aesthetics. 3D printing fosters a culture of innovation, positioning automotive companies at the forefront of technological advancement.
Challenges and Limitations
Limitations exist within the 3D printing landscape, impacting the automotive industry. Understanding these challenges is crucial for maximizing the potential of this technology.
Material Limitations
Material selection for 3D printing presents challenges. Not all materials suitable for traditional manufacturing processes work for 3D printing. For instance, some polymers may not endure the heat and stress encountered in automotive applications. Metal 3D printing, while advancing, often faces issues with strength and durability. Engineers can struggle with the lack of material certifications, complicating the approval process for components. Additionally, material costs may escalate, particularly for high-performance alloys, hindering wider adoption. Compounding these issues, 3D printing often involves limited choices regarding surface finish and visual aesthetics, affecting the final product’s marketability.
Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory frameworks pose significant challenges. Automotive parts must adhere to stringent safety standards, which vary across regions. Approval processes can consume considerable time and resources, impacting production timelines. As regulations evolve, manufacturers must stay informed about compliance requirements, which often lag behind technological advances. Lack of established testing protocols for 3D printed components introduces uncertainty for manufacturers. Certification processes can become lengthy, creating bottlenecks in innovation. Overall, navigating these regulatory landscapes requires careful planning and a proactive approach to ensure product readiness.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Automotive
Emerging trends in 3D printing for the automotive industry focus on advances in materials and processes. Smart materials with self-healing properties are being developed to enhance durability and safety in automotive parts. Innovations in biocomposite materials address sustainability concerns while maintaining high performance standards.
Customization continues to lead the way as manufacturers explore consumer preferences. This shift enables mass customization, allowing customers to tailor vehicles according to their specifications. Companies increasingly adopt cloud-based design platforms to facilitate collaboration, speeding up the entire production process.
Integration of artificial intelligence enhances the design and manufacturing phases. AI algorithms analyze performance data, optimizing designs for better efficiency and fewer defects. Automation in the printing process improves consistency and reduces manual labor, leading to more reliable outputs.
Increasing interest in lightweight components drives research into advanced printing techniques. Efficient lightweight structures contribute to better fuel efficiency, aligning with environmental regulations. The push for electric vehicles influences 3D printing’s role, as manufacturers seek to produce components that meet specific requirements for weight and energy efficiency.
Adoption of hybrid manufacturing models shows promising potential. These models combine traditional methods with 3D printing, increasing flexibility in production. As companies pivot towards on-demand production, they reduce waste and lower inventory costs.
Collaboration within the industry fosters a culture of innovation. Joint ventures between automotive firms and tech companies enhance material and process development. Companies remain committed to overcoming existing challenges like regulatory hurdles and material limitations, aiming for more streamlined approval processes and enhancing market viability.
3D printing is reshaping the automotive industry in profound ways. Its ability to streamline production processes and foster innovation is unmatched. As manufacturers embrace this technology they’re not only enhancing efficiency but also paving the way for sustainable practices within the sector.
The future holds exciting possibilities as advancements in materials and design continue to emerge. By addressing current challenges and leveraging collaborative efforts the automotive industry can fully harness the potential of 3D printing. This evolution promises to redefine how vehicles are designed and produced ultimately leading to more customized and efficient solutions for consumers.