In a world where everything seems to be getting faster, why should automotive parts be left behind? Enter 3D printing—the superhero of manufacturing that’s turning the automotive industry on its head. Forget waiting weeks for that elusive car part; with 3D printing, it’s like having a magic wand that produces components right before your eyes. Who knew technology could be so cool and efficient?
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of 3D Printing for Automotive Parts
3D printing transforms automotive part production, streamlining the manufacturing process. This technology produces complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve. Manufacturing time reduces significantly, often allowing for prototype creation within hours.
Cost efficiency becomes apparent as it minimizes material waste. Specific materials like thermoplastics, metals, and composites facilitate diverse applications in automotive parts. Examples include prototypes, custom components, and tools suited for specialized manufacturing needs.
Manufacturers adopt 3D printing to improve supply chain efficiency. On-demand production eliminates the need for large inventories, reducing storage costs.
Quality control benefits from 3D printing as it allows for iterative testing and adjustments before mass production. Automakers can quickly implement design changes based on real-time feedback. Moreover, the lightweight components produced contribute to fuel efficiency, enhancing overall vehicle performance.
Integration of 3D printed parts into current assembly lines occurs seamlessly, ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Companies utilizing these advancements experience shortened lead times, impacting overall project timelines positively.
Collaborative efforts between automotive companies and 3D printing firms foster innovation. Research initiatives focus on developing new materials and techniques, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in automotive manufacturing.
Investments in technology continue to rise, reflecting confidence in 3D printing’s potential. Automakers that leverage this technology establish a competitive edge in the market.
Benefits of 3D Printing in the Automotive Industry
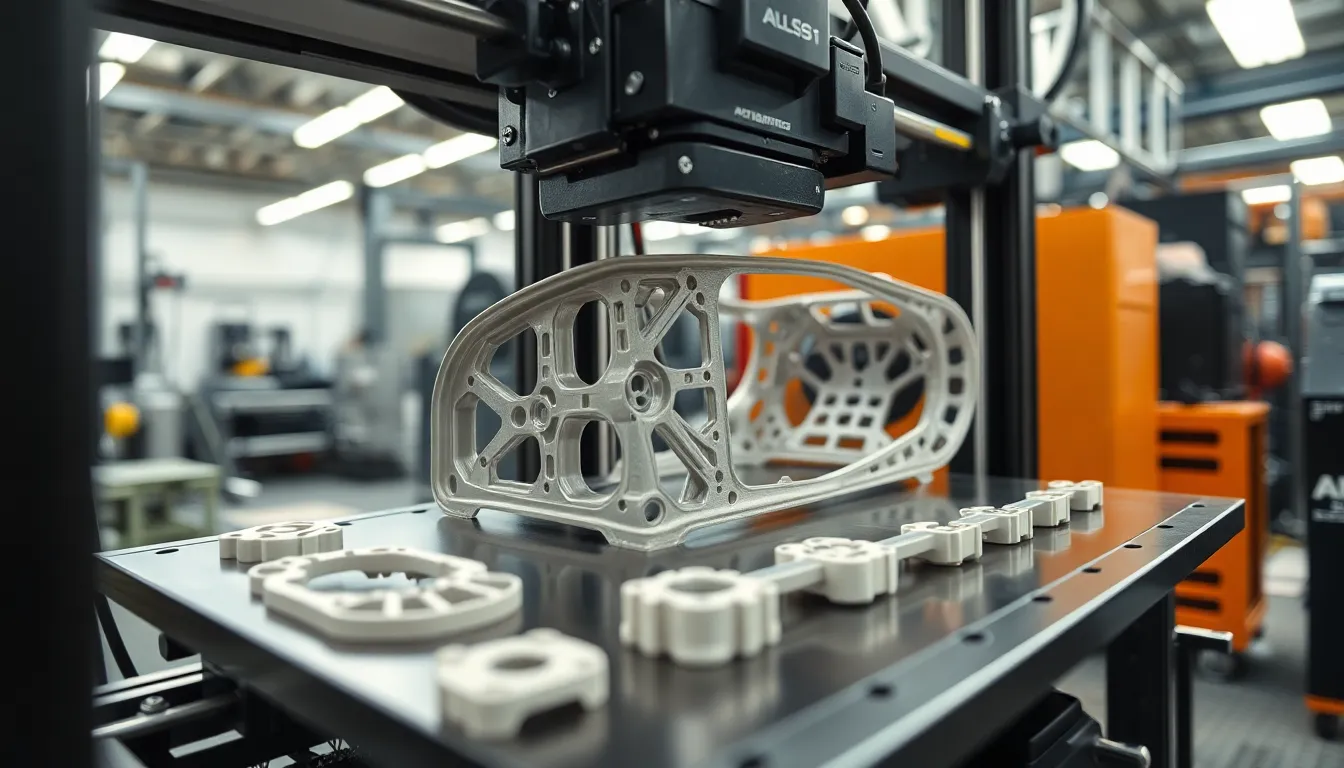

3D printing enhances various aspects of the automotive industry, providing advantages that boost efficiency and innovation. These benefits contribute to a paradigm shift in how manufacturers approach vehicle production.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency defines a key benefit of 3D printing. This technology significantly reduces production costs by minimizing material waste. Manufacturers often utilize only the necessary materials for each part, which cuts down on excess. Additionally, shorter lead times lower labor and operational expenses. Automakers also save on storage costs since on-demand production diminishes the need for large inventories. Research has shown that up to 90% savings occur in prototyping stages when using 3D printed components. Such savings allow for more budget flexibility in design and development phases, leading to a better return on investment.
Design Flexibility
Design flexibility represents another critical advantage of 3D printing. This technology enables the creation of complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to achieve. Engineers can design intricate components, which enhances performance and functionality. Rapid prototyping allows quick iterations based on real-time feedback, fostering a culture of innovation. Furthermore, the ability to customize parts for specific applications leads to improved fit and performance. As a result, automotive designers can push boundaries and explore new possibilities. Ultimately, this flexibility accelerates the development cycle and enhances product offerings.
Applications of 3D Printing in Automotive Parts
3D printing plays a crucial role in automotive applications, enhancing both prototyping and production processes.
Prototyping
Prototyping through 3D printing allows manufacturers to create functional models rapidly. Designers can produce complex geometries within hours instead of weeks. As a result, teams test designs early in the development cycle. Iterative feedback accelerates adjustments, ensuring designs meet performance criteria. This swift prototyping process reduces costs significantly, with studies showing potential savings of up to 90% in prototyping phases. Automotive companies embrace this technology to stay competitive, shortening the time from concept to market.
Production of End-Use Parts
Production of end-use parts benefits from 3D printing’s capacity for on-demand manufacturing. This approach decreases inventory costs since components are produced only as needed. Customization options expand, allowing manufacturers to tailor parts for specific vehicles or customer preferences. As such, automakers can implement lightweight materials that enhance fuel efficiency. Adoption of this technology leads to better supply chain efficiencies and shorter lead times. Furthermore, integration with existing production lines has been straightforward, ensuring a smooth transition to this innovative approach.
Challenges and Limitations
3D printing for automotive parts brings various challenges and limitations that manufacturers must navigate. Understanding these issues is essential for successful implementation.
Material Constraints
Material constraints significantly impact the effectiveness of 3D printing in automotive applications. Different materials possess unique properties that influence durability, strength, and heat resistance. Metals like aluminum and titanium offer superior performance but can present challenges in processing techniques. Thermoplastics, while versatile, may not withstand high-stress conditions found in critical components. Creating parts that meet necessary performance criteria requires careful selection and testing of materials. Not all materials are compatible with 3D printing processes, limiting options for certain applications. As manufacturers experiment with new materials, ongoing research aims to expand capabilities and overcome these limitations.
Regulatory Standards
Regulatory standards pose significant challenges in the widespread adoption of 3D printing in the automotive sector. Strict guidelines govern safety, performance, and environmental impacts, requiring manufacturers to comply before incorporating 3D printed components. Meeting these standards often necessitates extensive testing and validation processes, which can lead to increased costs and longer lead times. Variations in regulations across different markets complicate matters further, as each region may impose specific requirements. Companies must invest in understanding these standards to avoid penalties and ensure consumer safety. Adaptation to evolving regulations is crucial, as technology progresses and the demand for 3D printed parts increases.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Automotive Parts
Advanced 3D printing technologies are poised to redefine automotive manufacturing. Customization options cater to unique customer specifications, enhancing personalization in vehicle design. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning optimizes the design process, enabling smarter production techniques.
Sustainability initiatives influence material choices, as manufacturers shift to bio-based and recycled materials. Lightweight components made through 3D printing contribute significantly to fuel efficiency and overall performance. Additionally, as the demand for electric vehicles increases, 3D printing will support the development of specialized parts tailored for electric drivetrains.
Adoption of hybrid manufacturing techniques blends traditional and additive methods, improving efficiency while leveraging existing infrastructure. Collaboration between automotive companies and 3D printing firms accelerates research into new materials and printing technologies, fostering innovation.
Real-time data analytics allows for continuous improvement in production processes. Continuous feedback loops streamline quality control, ensuring that parts meet industry standards consistently. Moreover, investment in workforce training highlights the need for skilled professionals to manage and operate advanced 3D printing technologies.
Regulations continue to evolve, impacting the materials and processes used in 3D printed parts. Manufacturers will face the challenge of ensuring compliance while maximizing production capabilities. As standards become more stringent, integrating safety and performance measures into the design stage remains crucial.
Lastly, as the market for aftermarket parts grows, 3D printing will enhance the availability of hard-to-find components. On-demand manufacturing reduces reliance on large inventories, effectively lowering costs and improving customer satisfaction. Exploring these trends will be essential for automotive companies looking to remain competitive in a rapidly changing landscape.
The automotive industry is on the brink of a revolution thanks to 3D printing technology. As manufacturers embrace this innovation, they’re not only enhancing efficiency but also redefining design possibilities. The ability to produce complex parts quickly and cost-effectively sets a new standard in automotive production.
Future advancements will likely focus on sustainability and customization, further elevating the role of 3D printing in the sector. As companies navigate challenges and invest in new techniques, the potential for improved performance and customer satisfaction becomes increasingly attainable. The integration of 3D printing into automotive manufacturing is more than just a trend; it’s a strategic move shaping the future of the industry.